NASA website exposed to serious vulnerability
A serious security vulnerability exists in the NASA astrobiology-specific website that could trick users into visiting a malicious site by disguising a dangerous URL with the NASA name.
Space travel is undoubtedly dangerous. However, it can also be so when visiting NASA websites. the Cybernews research team discovered an open redirect vulnerability in the NASA Astrobiology website.
As a result of the researchers' investigation, the vulnerability had already been discovered and reported by researchers through the Vulnerability Bounty Program several months earlier (January 14, 2023), but was not addressed and fixed by the agency.
An attacker could use this vulnerability to redirect anyone to a malicious website to obtain their login credentials, credit card numbers or other sensitive data.
The Cybernews research team has contacted NASA several times since early April and has not received any response as of today.
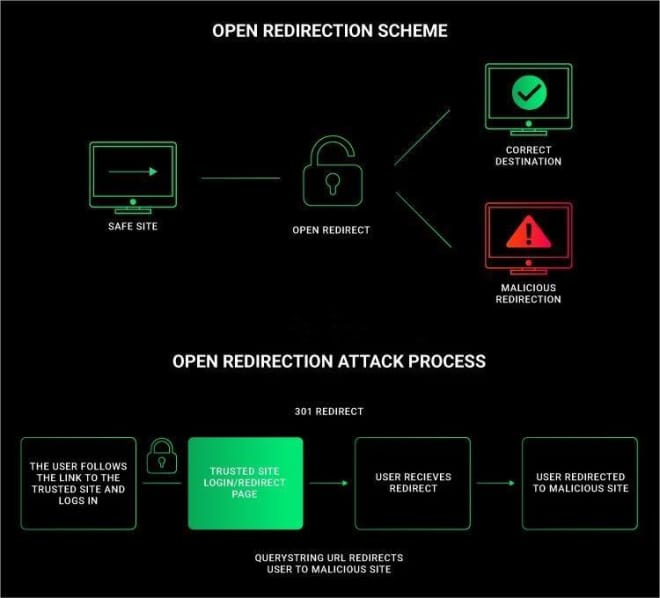
What is an open redirect vulnerability?
An open redirection vulnerability is simply like a fake cab driver. For example, you hail a cab and tell the driver where you want to go, but instead of dropping you off at your destination, he takes you to another location.
Similarly, a user trying to access astrobiology.nasa.gov could be redirected to a malicious website. Typically, web applications validate user-supplied input, such as URLs or parameters, to prevent malicious redirects from occurring.
An attacker could exploit the vulnerability by disguising a malicious URL as a legitimate URL to lure users to a malicious website or phishing page, the Web News researchers explained.
Why is the open redirect vulnerability dangerous?
An attacker could modify NASA's website with additional parameters to direct users to the place of their choice. The redirected site could even resemble a NASA page, only with a prompt asking for credit card data.
In addition, an attacker could exploit an open redirection vulnerability to direct users to the site and download malware to their computer or mobile device immediately after logging in.
Another way to exploit the vulnerability is to control search engine rankings by redirecting users to sites that display low-quality content or spam.
While we have not confirmed if anyone has actually exploited this vulnerability on NASA's website, the vulnerability has in fact been exposed for several months.
How to mitigate the impact of the open redirect vulnerability?
Exploiting an open redirect vulnerability could allow malicious actors to conduct phishing attacks, steal credentials and spread malware.
To avoid such incidents, it is highly recommended that websites validate all user input, including URLs.
This may include using regular expressions to verify the correct format of the URL, checking that the URL is from a trusted domain, and verifying that the URL does not contain any additional or malicious characters.
To prevent malicious characters from being injected into URLs, webmasters can also use URL encoding. Also, website owners can create a whitelist of trusted URLs and only allow redirects to these URLs. prevent attackers from redirecting users to malicious or unauthorized websites.
【Dark Web】●5 Awesome Dark Web Links
銆怬pen Source Intelligence銆戔棌5 Hacking Forums Accessible by Web Browsers
【Web Intelligence Monitoring】●Advantages of open source intelligence
【News】●AI-generated fake image of Pentagon explosion goes viral on Twitter
【Open Source Intelligence】●10 core professional competencies for intelligence analysts
銆怤etwork Security銆戔棌9 popular malicious Chrome extensions



