AI-generated fake image of Pentagon explosion goes viral on Twitter
Recently, an AI-generated fake image of a violent explosion at the Pentagon in Washington, D.C., went viral on Twitter. The incident exposed the real problem with Musk's paid Twitter Blue verification.
The fake image went viral online shortly after it was posted on the social messaging platform late on the morning of May 22, and was only quelled when U.S. government officials came forward, confirming and denouncing the image as nothing more than a hoax.
The matter was controversial after blue check marks appeared next to the profile names of Russian state media and a fake Bloomberg News account.
Around 10 a.m. ET, a photo of a blazing Pentagon lawn with the caption "Large Explosion near The Pentagon Complex in Washington D.C. - Initial Report." began to be heavily reposted and quickly spread.
According to Forbes, a U.S. Department of Defense spokesman has declared the photo to be "misinformation.
By 10:27 a.m. ET, Arlington Fire and EMS also denounced the photo as a fake on Twitter. The department's Twitter account posted that @PFPAOfficial and ACFD were aware of social media reports circulating online of an explosion near the Pentagon, but that no explosions had occurred on or near the Pentagon Reservation that would pose an immediate danger or hazard to the public.
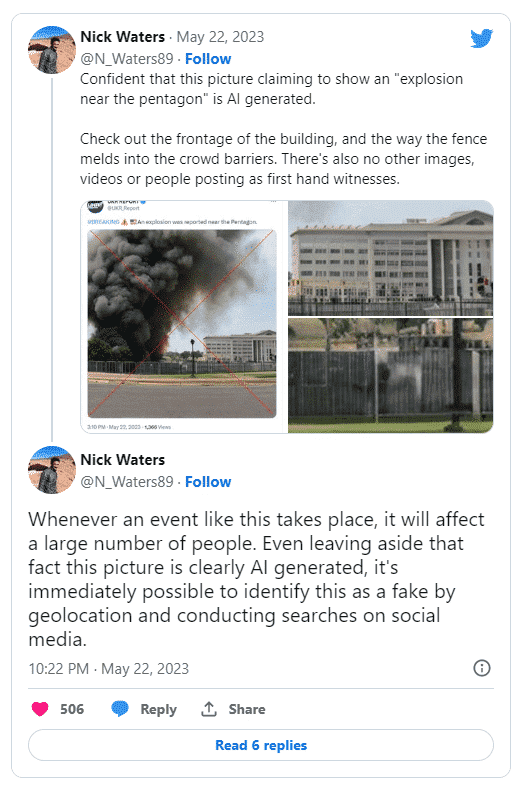
OSINT experts thoroughly examined the images within minutes and pointed out discrepancies that proved the images were indeed fake images generated by AI.
Nick Walters, a digital investigator at Bellingcat, said it would be very difficult, if not impossible, to fake such an event. This can be easily determined by looking at the front of the building in the image and the way the fence blends into the crowd barrier.
Nick Walters says that for such a major news story, it is not as credible without other first-hand eyewitness photos or videos posted online.
In addition, Nick Walters tweeted that most extreme physical events ( bombings, terrorist attacks, large fights) in densely populated areas create recognizable digital ripples.
Fake AI images, while fun for creators and viewers, have been one of the biggest concerns for governing entities and AI experts since the release of ChatGPT last November.
Earlier in May, a man was arrested in China and faces up to 10 years in prison for using deep technology to spread fake news online. The man is accused of using ChatGPT to create a fake artificial intelligence news video that depicted a fatal train collision and then posting it on multiple social media sites.
With artificial intelligence models evolving in recent years, experts say disinformation on social media is very concerning, especially with the 2024 U.S. presidential election cycle just beginning.
Andy Campbell, senior editor at The Huffington Post, referenced the struggle Twitter CEO Musk had with Twitter users over his Twitter Blue verification when he took over the company last fall.
It used to be that a social media company was able to prove the legitimacy of an organization or individual before its account was granted Twitter's Blue checkmark, but now it's granted for free to anyone willing to pay $8 a month.
The controversial situation on this issue reached its peak in March when many formerly certified celebrities and journalists refused to pay for a service that was once free and said they could have this certified blue checkmark removed from their accounts.
Andy Campbell says the danger of this blue checkmark pay-for-verification system is that if an account tweets an AI-generated fake news photo about the Pentagon explosion, but with authentication, at first glance the account looks like a legitimate Bloomberg News tweet.
That fake Bloomberg News account has been deactivated by Twitter, but it is still not known where the fake Pentagon picture came from. Although, the fake Pentagon bombshell news went viral briefly, the rumor still led to a big drop in the New York Stock Exchange on Monday.
銆怤ews銆戔棌Access control giant hit by ransom attack, NATO, Alibaba, Thales and others affected
【Web Intelligence Monitoring】●Advantages of open source intelligence
銆怤etwork Security銆戔棌9 popular malicious Chrome extensions
【Artificial Intelligence】●Advanced tips for using ChatGPT-4
【Dark Web】●5 Awesome Dark Web Links
銆怰esources銆戔棌The Achilles heel of AI startups: no shortage of money, but a lack of training data



