Critical OAuth vulnerability in the Expo framework allows account hijacking
A critical security vulnerability has been disclosed in the Open Authorization (OAuth) implementation of the application development framework Expo. io.
The vulnerability has a CVE identifier of CVE-2023-28131 and a severity rating of 9.6 on the CVSS rating system. API security firm Salt Labs said the issue is served using a framework vulnerable to credential leakage, which could then be used to hijack accounts and siphon sensitive data.
In some cases, threat actors could exploit the flaw to perform arbitrary actions on behalf of infected users on various platforms, such as Facebook, Google or Twitter.
Expo is similar to Electron, an open source platform for developing general-purpose native applications that run on Android, iOS and the Web.
It is important to note that for the attack to be successful, sites and applications using Expo should use third-party providers such as Google and Facebook to configure AuthSession proxy settings for single sign-on (SSO).
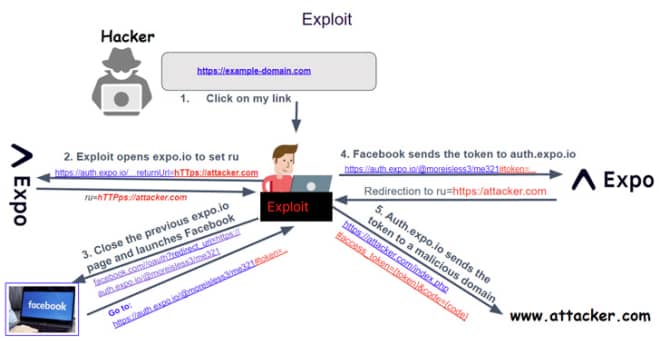
In other words, the vulnerability can be exploited to send a secret token associated with a login provider (such as Facebook) to a domain controlled by the participant and use it to seize control of the victim's account.
In turn, this is accomplished by tricking the targeted user into clicking on a specially crafted link that can be sent via traditional social engineering vectors such as email, SMS or suspicious websites.
In an announcement, Expo said it deployed a patch within hours of the responsible disclosure on Feb. 18, 2023. Users were also advised to migrate from using the AuthSession API proxy to registering a deep-link URL scheme directly with a third-party authentication provider to enable SSO functionality.
The vulnerability could allow a potential attacker to trick users into visiting a malicious link, logging in to a third-party authentication provider and inadvertently compromising their third-party authentication credentials, said James Ide of Expo. This is because auth.expo.io used to store the application's callback URL before the user explicitly confirmed that they trusted the callback URL.
The disclosure follows the discovery of similar OAuth issues in Booking.com (and its sister site Kayak.com) that could have been used to take control of users' accounts, gain full knowledge of their personal or payment card data, and perform actions on behalf of victims.
A few weeks ago, Swiss cybersecurity firm Sonar detailed a path traversal and SQL injection flaw in the Pimcore enterprise content management system ( CVE-2023-28438 ) that could be abused by attackers to run arbitrary PHP code on a server and gain access to the following privileged web server.
Back in March 2023, Sonar also disclosed an unauthenticated stored cross-site scripting vulnerability affecting LibreNMS 22.10.0 and earlier, which can be exploited to obtain remote code execution when Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is enabled.
【News】●AI-generated fake image of Pentagon explosion goes viral on Twitter
銆怤ews銆戔棌Access control giant hit by ransom attack, NATO, Alibaba, Thales and others affected
【Web Intelligence Monitoring】●Advantages of open source intelligence
【Dark Web】●5 Awesome Dark Web Links
【Open Source Intelligence】●10 core professional competencies for intelligence analysts
銆怰esources銆戔棌The 27 most popular AI Tools in 2023
銆怬pen Source Intelligence銆戔棌5 Hacking Forums Accessible by Web Browsers



