What is due diligence?
Related:
Benefits of
open source intelligence for due diligence
The corporate world
is ever-changing and high-stakes, and a clear understanding of what's going on can
make the difference between success and failure. Even a minor oversight can derail a
multi-billion dollar deal, so it's critical to have the right information and know
who you're dealing with. That's where due diligence comes in.
What
is due diligence?
Due diligence has become synonymous with
business risk assessment, but what does the term really mean? In short, the due
diligence process involves verifying, investigating and auditing a potential
transaction or investment opportunity to confirm all relevant facts and data,
financial or otherwise. It is the investigative part of the Know Your Customer (KYC)
process and is an important part of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
Due diligence is critical for Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) transactions.
It allows investors to determine the financial viability of the acquisition and
identify any issues with the target company's operations. By conducting a thorough
investigation, decision makers can make an informed choice about the viability of
the arrangement. Given that the outcome can have a significant impact on the success
of the investment, companies recognize the importance of this process.
In a
broad sense, we can talk about three different types of due diligence:
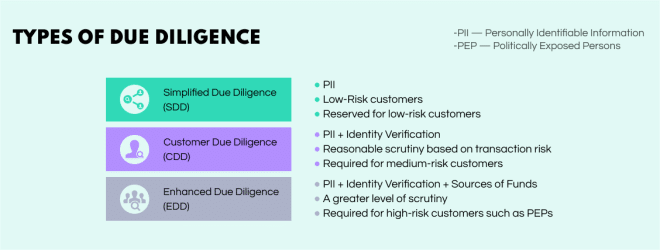
1.
Simplified due diligence (SDD)
The lowest form of due
diligence that an institution can conduct. It is applied in cases where criminal
risk is slim to none and covers a superficial verification of the person’s identity.
2. Customer due diligence (CDD)
The most common
form of due diligence aims to detect risk and prevent money laundering. It's
actually a legal requirement, with companies facing penalties if they neglect to
conduct CDD checks. Corporations failing to meet the requirements may be fined
$560-2240 per violation.
3. Enhanced due diligence (EDD)
What makes EDD checks different from CDD processes is the level of scrutiny.
Customer due diligence identifies the subject but does not verify their claims.
Enhanced due diligence goes into much more detail to track, analyze, and consider
every aspect of the subject’s financial life to minimize any potential risk. While
EDD also aims to detect risk and prevent criminal wrongdoing, it’s reserved for
high-risk individuals and businesses due to location, occupation, and political
exposure.