Best Intelligence Analysis Tools
In today's data-driven world, intelligence analysis is crucial for extracting actionable insights from vast and varied data sources. Analysts utilize sophisticated tools and technologies to process, interpret, and visualize information, enabling them to identify patterns and trends that inform strategic decision-making. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the accuracy of intelligence reports but also improves the efficiency and effectiveness of analytical processes. By leveraging these advanced tools, analysts can transform raw data into meaningful insights, driving better outcomes across various sectors.
Sources Used in Intelligence Analysis
Intelligence analysis involves transforming raw data into actionable insights that are crucial for national security. Intelligence analysts gather and scrutinize information to produce intelligence briefs, which help identify threats and guide decision-making processes.
The essence of intelligence analysis lies in evaluating data to draw conclusions that protect national security. Analysts gather information from a variety of sources to combat terrorism, organized crime, and cyber threats.
Analysts rely on a multitude of sources, often cross-referencing to validate their conclusions. The primary sources include:
Human-source intelligence (HUMINT)
Human sources are pivotal for intelligence agencies. Utilizing HUMINT effectively demands a thorough understanding of the source's reliability and potential vulnerabilities.
Geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) and imagery intelligence (IMINT)
This form of intelligence involves satellite or aerial reconnaissance. Analysts need advanced technical skills to interpret geospatial and imagery data.
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) and signals intelligence (SIGINT)
These intelligence forms focus on technical data to locate or identify targets. For instance, SIGINT is gathered by intercepting signals to track networks, requiring analysts to have robust technical and analytical capabilities.
Open source intelligence (OSINT)
OSINT relies on publicly accessible sources like the internet and social media. Newspapers, online databases, and public videos are valuable, and analysts need strong data processing skills to extract relevant information.
Effective intelligence analysis hinges on credible sources. Without them, analysts cannot produce reliable conclusions about risk mitigation, threat assessment, and security targets.
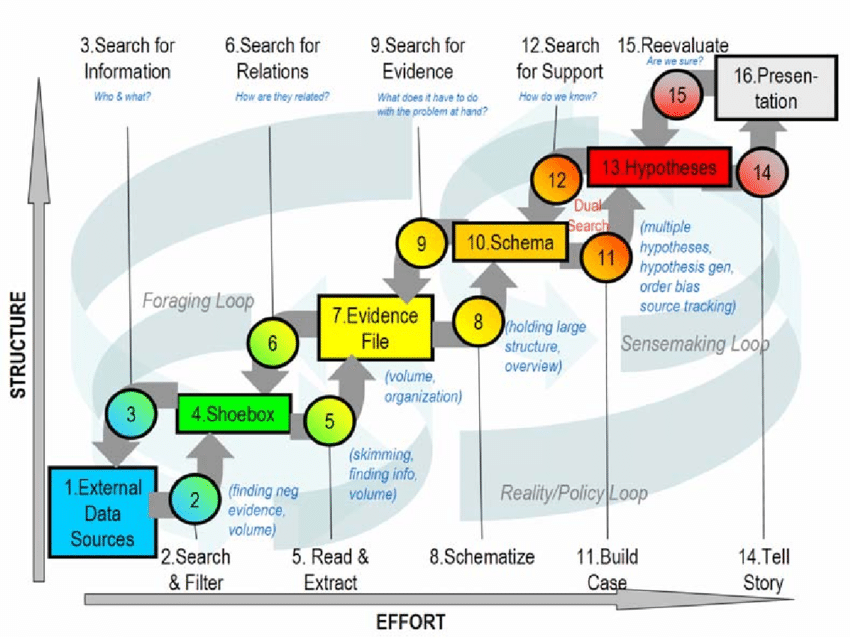
Goals of Intelligence Analysis
Intelligence analysts use various tools and techniques to gather intelligence. Their ultimate goals include:
Evaluate Sources
Reliable intelligence necessitates credible information. The analysis process involves assessing the reliability of sources and the methods used to collect data.
Identify Vulnerabilities
Analysts identify potential targets and vulnerabilities within the United States to safeguard national security. This process also includes recognizing gaps in intelligence sources to enhance reports.
Threat Assessment
Analysts evaluate information to judge the threat posed by foreign actors, hackers, and other adversaries. Sharing raw intelligence with allies is also crucial for comprehensive threat assessment.
Risk Mitigation
Analysts provide intelligence to decision-makers to mitigate risks and prevent attacks. This involves addressing vulnerabilities before adversaries can exploit them.
Beyond collecting and processing data, the intelligence community advises on strategies to protect national security and counter threats.
Advanced Technologies in Intelligence Analysis
Intelligence analysis tools are indispensable in the field of intelligence gathering and analysis. They empower analysts to process, interpret, and visualize vast amounts of data efficiently. By leveraging advanced technologies, these tools enhance decision-making processes and enable analysts to derive meaningful insights from various information sources.
A primary function of intelligence analysis tools is data collection and integration. These tools can gather data from diverse sources, including open-source intelligence (OSINT), human intelligence (HUMINT), signals intelligence (SIGINT), and geospatial intelligence (GEOINT). Once collected, the data is integrated and organized into a centralized repository, simplifying access and analysis. Automation of data collection further saves analysts considerable time and effort.
After data collection, intelligence analysis tools employ various analytical techniques to extract relevant information and identify patterns and relationships. Techniques such as text mining, data mining, link analysis, social network analysis, sentiment analysis, and statistical analysis are commonly used. These methods help analysts uncover hidden insights, detect anomalies, and identify trends crucial for informed decision-making.
Visualization is another critical feature of intelligence analysis tools. They enable analysts to represent complex data in visual formats such as charts, graphs, maps, and timelines. Visualizations assist in identifying spatial and temporal patterns, understanding relationships, and presenting findings clearly and concisely. Interactive visualizations further enhance analysis by allowing analysts to drill down into data, filter information, and generate customized reports.
Collaboration and information sharing are essential in intelligence analysis. These tools facilitate seamless collaboration among analysts and agencies through features like shared workspaces, real-time updates, commenting, and document sharing. Such features enable analysts to collectively work on cases, share findings, discuss hypotheses, and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the intelligence picture.
Security and confidentiality of information are paramount in intelligence analysis. Intelligence tools implement rigorous security measures to protect classified information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. They use encryption, access controls, audit logs, and secure communication protocols to safeguard sensitive data.
Tools Used by Intelligence Analysts
Intelligence analysts rely on a wide range of tools and technologies to efficiently process large volumes of data and extract valuable insights. These tools help analysts collect, analyze, and disseminate information effectively, ensuring timely and informed decision-making. From data mining software to satellite imagery, the evolution of these tools is crucial to the success of intelligence operations.
Data Mining Software
Data mining software enables analysts to sift through vast amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and significant information. This capability allows for the rapid identification of potential threats and risks, facilitating the development of effective mitigation strategies.
RapidMiner is a robust data mining and machine learning platform that helps analysts uncover actionable insights from large datasets. RapidMiner supports a wide range of data sources and provides powerful visualization tools, making it easier to interpret complex data. It also offers automated machine learning features, which can significantly speed up the analysis process and improve accuracy.

Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS technology allows analysts to visualize and analyze geographical and locational data. This is particularly useful for mapping strategic locations such as military bases or critical infrastructure, aiding in threat assessment and strategy formulation.
ArcGIS by Esri is a leading GIS platform that enables detailed mapping and spatial analysis. ArcGIS offers real-time data integration and advanced geoprocessing capabilities, which are crucial for dynamic intelligence operations. Additionally, its intuitive interface and comprehensive toolset make it accessible for users with varying levels of expertise.
Social Media Monitoring Tools
In the digital age, social media monitoring tools are essential for tracking potential threats and risks on social platforms. These tools help analysts identify key influencers and monitor conversations for early warning signs of violent or extremist behavior.
Knowlesys offers advanced social media monitoring solutions that help analysts track and analyze social media activity for threat intelligence. Knowlesys provides real-time monitoring and sophisticated filtering options, allowing for precise and targeted analysis. Its ability to integrate with other intelligence tools enhances its utility in comprehensive threat analysis.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery provides analysts with a bird's-eye view of the earth, allowing for the monitoring of terrain changes, military movements, and other critical features. This technology is invaluable for identifying missile sites, tracking vehicle movements, and observing changes in sensitive areas.
Google Earth Pro offers advanced satellite imagery viewing and analysis features. Google Earth Pro includes historical imagery capabilities, which enable analysts to observe changes over time. Its high-resolution imagery and user-friendly interface make it an essential tool for detailed spatial analysis.
Cryptography Tools
Cryptography tools are essential for decoding and interpreting encrypted messages. These tools use complex algorithms to crack codes, which is vital for intelligence agencies monitoring communications from foreign governments or terrorist groups.
VeraCrypt is a free, open-source disk encryption software that enhances security for encrypted data. VeraCrypt supports a variety of encryption algorithms and can secure entire disk partitions as well as individual files. Its robust encryption standards and ease of use make it a preferred choice for secure data handling.
Threat Intelligence Platforms
These platforms aggregate and analyze threat data from multiple sources, enabling analysts to identify and respond to potential threats effectively.
MISP (Malware Information Sharing Platform) is an open-source threat intelligence platform that helps collect, share, and correlate threat data. MISP provides advanced sharing capabilities and customizable threat feeds, enhancing collaboration among intelligence communities. Its open-source nature ensures continuous improvement and adaptability to emerging threats.
OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) Tools
OSINT tools are crucial for gathering information from publicly available sources, including websites, social media, and forums.
OpenCTI (Open Cyber Threat Intelligence) is an open-source platform for managing and analyzing cyber threat intelligence. OpenCTI integrates seamlessly with other intelligence tools and provides a comprehensive framework for threat data management. Its collaborative features and extensive documentation support a wide range of intelligence operations.
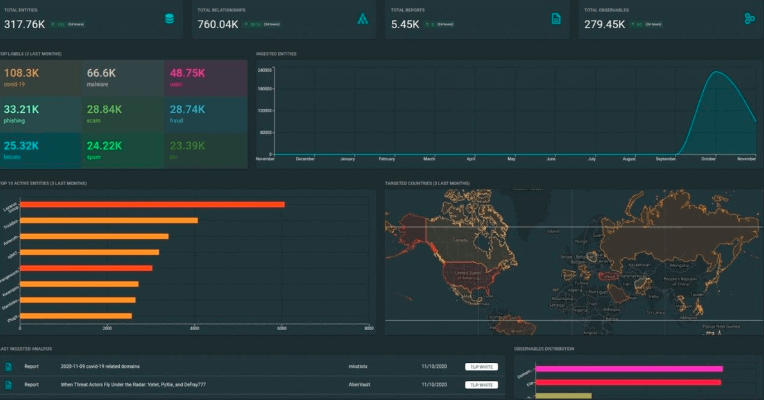
Malware Analysis Tools
These tools help in analyzing malware samples to understand their behavior and potential impact.
Cuckoo Sandbox is an open-source automated malware analysis system. Cuckoo Sandbox provides detailed reports on malware behavior, including network activity, file modifications, and registry changes. Its extensibility and support for various virtualization environments make it a versatile tool for in-depth malware analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of intelligence analysis is ever-evolving, with advanced tools and technologies playing a pivotal role in enhancing analytical capabilities. From data mining and GIS to social media monitoring and cryptography, these tools enable analysts to efficiently process vast amounts of data, uncover hidden patterns, and derive meaningful insights. The collaborative features and rigorous security measures embedded in these tools ensure that analysts can work together seamlessly while safeguarding sensitive information. As threats continue to evolve, staying ahead with cutting-edge intelligence analysis tools is essential for informed decision-making and effective threat mitigation.