The Power and Evolution of Electronic Surveillance
Electronic surveillance has profoundly reshaped how societies monitor and gather information, evolving from the simplistic systems of the past to the sophisticated technologies of today. Understanding the progression of electronic surveillance is crucial to comprehending its current capabilities and anticipating future advancements.

What is Electronic Surveillance?
Electronic surveillance refers to the monitoring and collection of digital traces left by individuals. This can be achieved through various methods, such as tracking someone's movements via CCTV, reading their text messages, analyzing their internet browsing history and social media activities, or even covertly activating webcams or microphones to spy on them.
Electronic surveillance can serve multiple purposes. It might be a focused operation conducted by a government as part of a criminal investigation, or it could be part of a broader initiative known as mass surveillance aimed at monitoring internet usage on a large scale. These surveillance activities are designed to achieve different objectives, such as gathering evidence against suspected criminals or keeping tabs on dissidents opposing a government.
Physical and Electronic Surveillance: An Overview
Physical Surveillance
Physical surveillance is one of the most traditional methods used by law enforcement. When authorities suspect an individual of illicit activities, they often follow them to gather evidence. However, most countries impose strict limitations on physical surveillance to protect privacy rights, especially within private homes. The conditions under which government authorities can conduct physical surveillance depend on the jurisdiction and typically require judicial authorization based on criteria like probable cause or reasonable suspicion.
Electronic Surveillance
Unlike physical surveillance, electronic methods allow for collecting a broader range of evidence without direct physical presence. Due to its intrusive nature, electronic surveillance is subject to stringent legal controls and is typically considered only when less intrusive methods are ineffective or unavailable. Despite its potential for abuse, electronic surveillance is widely supported in combating serious crimes like organized crime and terrorism.
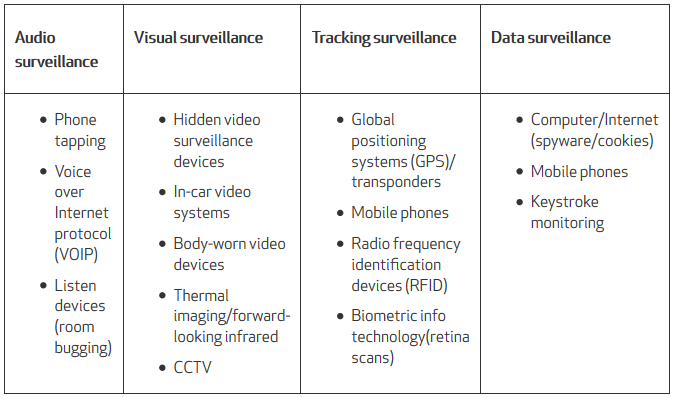
Forms of Electronic Surveillance
Audio Surveillance
Phone Tapping: Intercepts phone conversations.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP): Monitors internet-based calls.
Listening Devices: Used for room bugging.
Visual Surveillance
Hidden Cameras: Discreet video recording.
In-car Video Systems: Surveillance within vehicles.
Body-worn Cameras: Used by law enforcement personnel.
Thermal Imaging: Detects heat signatures.
CCTV: Monitors public and private spaces.
Tracking Surveillance
GPS: Tracks location and movement.
Mobile Phones: Monitors activities and locations.
RFID: Tracks items and individuals using radio frequencies.
Biometric Technology: Uses retina scans for identification.
Data Surveillance
Internet Monitoring: Tracks online activities using spyware or cookies.
Mobile Phones: Monitors calls, messages, and app usage.
Keystroke Monitoring: Records keyboard inputs to track digital activities.
Why You Might Need Electronic Surveillance?
Protecting Sensitive Information
In today's digital world, protecting sensitive information is crucial. This includes business secrets, personal financial data, and confidential conversations. Individuals and organizations often need electronic surveillance detection to ensure their private information remains secure. By identifying potential eavesdropping devices or other forms of surveillance, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard their data, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring confidentiality.
Preventing Corporate Espionage
Corporate espionage poses a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. Competitors may resort to spying to gain an edge, often using listening devices, hidden cameras, or other surveillance methods. Electronic surveillance detection helps businesses uncover any espionage attempts, thereby protecting their intellectual property and maintaining a competitive advantage. Detecting and mitigating these risks early can prevent substantial financial and reputational damage.
Safeguarding Personal Privacy
Maintaining personal privacy has become increasingly challenging with the proliferation of smart home devices, social media, and other digital technologies. People may be unaware of who is watching, listening, or tracking their activities. Electronic surveillance detection assists in identifying privacy breaches, such as hidden cameras or tracking devices. By detecting these breaches, individuals can take appropriate actions to protect their personal information and maintain their privacy.
Preventing Stalking and Harassment
Stalking and harassment are severe issues that can be exacerbated by electronic surveillance. Victims may fear that their stalkers are using electronic devices to monitor their movements and activities. Electronic surveillance detection can help identify any such devices, allowing individuals to take necessary steps to ensure their safety and well-being. By addressing these threats promptly, victims can seek legal protection and improve their personal security.
Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Laws
Many countries have stringent privacy laws regulating electronic surveillance. Failure to comply with these laws can result in severe legal consequences for individuals and businesses. Professional electronic surveillance detection ensures that surveillance activities adhere to legal standards. By detecting and removing unauthorized surveillance devices, individuals and organizations can avoid unintentional violations of privacy laws, thereby ensuring legal compliance and protecting themselves from potential penalties.
Who Conducts Electronic Surveillance?
The primary actors involved in electronic surveillance are intelligence agencies and other government departments. These entities have the resources and capabilities to monitor large groups of people, both domestically and internationally. Beyond intelligence agencies, regular law enforcement agencies also engage in electronic surveillance.
In addition to governments, numerous companies track online activities for commercial purposes. These companies collect extensive data to generate revenue, often by selling information about people's browsing habits to advertisers for more targeted marketing. While this type of tracking may not fit the traditional definition of surveillance, many critics argue that it infringes on the privacy of internet users. Additionally, companies use electronic surveillance to monitor employee activities during work hours.
The Evolution of Electronic Surveillance: Past, Present, and Future
The Past: Genesis of Electronic Surveillance
The origins of electronic surveillance can be traced back to the analog era, with the introduction of closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras. These early systems were foundational in the realm of electronic monitoring, providing a basic but essential form of surveillance. Despite their significance, these early CCTV systems had limited capabilities. They were stationary, had low image quality, and required manual monitoring, which greatly hindered their effectiveness and range of application.
As technological advancements were made, the surveillance landscape underwent a significant transformation. The shift from analog to digital technology brought about clearer images, more accessible storage solutions, and the ability to remotely access surveillance footage. The advent of the internet further revolutionized the field by enabling real-time monitoring and significantly enhancing the scope and capabilities of surveillance systems. Although these early systems seem rudimentary compared to today's standards, they were crucial in setting the stage for the sophisticated electronic surveillance technologies we now have.
The Present: Technological Prowess and Integration
Today, electronic surveillance is characterized by cutting-edge technological advancements. High-definition cameras provide clear and detailed footage, while artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics have revolutionized the way surveillance data is processed and utilized. Modern surveillance systems now incorporate smart sensors, facial recognition technology, and machine learning algorithms, which have greatly increased their efficiency and effectiveness.
The integration of these advanced technologies has made surveillance systems more intelligent and capable. AI-driven video analytics can automatically detect and respond to suspicious activities, while machine learning enables systems to learn from past data and improve their accuracy over time. This technological prowess has made electronic surveillance an indispensable tool in various sectors, including law enforcement, public safety, and private security.
The Future: Anticipating Trends and Challenges
Looking towards the future, the field of electronic surveillance is poised for even greater advancements. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to create interconnected surveillance systems that can adapt to dynamic environments. This will allow for more comprehensive and real-time monitoring across various locations and devices.
Artificial intelligence will continue to play a pivotal role in the evolution of electronic surveillance. Future advancements in AI will lead to the development of more sophisticated predictive algorithms, capable of foreseeing potential threats before they occur. This proactive approach to surveillance will enhance security measures and allow for timely interventions.
Moreover, the emergence of smart cities and connected spaces will further drive the adoption and advancement of electronic surveillance technologies. As urban environments become more interconnected, the role of surveillance in ensuring safety and security will become increasingly critical. The continuous research and development in this field will ensure that surveillance systems remain at the forefront of technological innovation, ready to meet the challenges of an ever-evolving security landscape.
Conclusion
The journey of electronic surveillance from its analog beginnings to its digital future highlights its critical role in security and privacy. As technology advances, the importance of robust surveillance detection measures will only grow, ensuring the protection of sensitive information and compliance with privacy laws. This evolving landscape demands continuous adaptation and vigilance to safeguard individual privacy and uphold legal standards while harnessing the benefits of cutting-edge surveillance technologies.