OSINT for Intelligence Agencies: A Comprehensive Guide
An intelligence agency is a government agency responsible for the collection, analysis, and exploitation of information in support of law enforcement, national security, military, and foreign policy objectives. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) has become an indispensable tool for intelligence agencies worldwide. In an era where data is abundant and readily accessible, intelligence agencies have increasingly turned to OSINT to gather, analyze, and interpret information.
Case Studies in OSINT for Intelligence Agencies
In the Ukrainian countryside, a lone individual with a cell phone and an internet
connection takes a video of the Russian column that advances further into
Ukrainian territory. With a tap of their screen, that video is shared to
Telegram, Instagram, Twitter, Facebook and a plethora of social media sites.
Within seconds that video is shared by others and within minutes, hundreds, if
not thousands have seen the footage. This footage would land in the hands of
ordinary individuals, as well as the Ukrainian Ministry of Defense.
This is an example of a phenomenon known as Open Source Intelligence or
OSINT. In its most basic forms, traditional intelligence gathering would rely on
agents or actors working for a certain government to collect information, with
the information usually being hidden from the public. OSINT on the other hand
relies on anyone on the ground, with the information being collected available
to anyone with an internet connection. There are many methods that the OSINT
community uses to report ongoing conflicts. A common thing seen in OSINT
communities is geolocating areas where videos take place using software such as
Google Earth. Terrain features such as coastlines, mountains and roads are
matched with footage taken from the conflict zone. The opening salvos of the
Russian invasion of Ukraine were captured by OSINT sites when webcam footage of
a border checkpoint near Crimea showed Ukrainian soldiers running away from
their post as Russian soldiers advanced. However, while OSINT may sound like an
extremely valuable asset, it should be used hand in hand with traditional
intelligence as a tool for intelligence agencies.
KIS (Knowlesys Intelligence System) offers several capabilities to help intelligence agencies overcome the challenges of OSINT
1. Data Filtering and Analysis: KIS uses AI to automatically filter and analyze vast amounts of data, helping to manage information overload and identify relevant intelligence quickly.
2. Accuracy and Verification: The system employs advanced algorithms for content analysis, author analysis, and fake account detection, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the information collected.
3. Multilingual Support: KIS can process multilingual content, breaking down language barriers and enabling comprehensive intelligence gathering from diverse sources.
4. Access to Restricted Information: By integrating various data sources, KIS can access and analyze information from a wide range of platforms, including those with restricted access.
5. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: The system provides real-time monitoring and early warning alerts for sensitive information, allowing agencies to respond promptly to emerging threats.
6. Legal and Ethical Compliance: KIS is designed to operate within legal and ethical boundaries, ensuring that the intelligence gathered is compliant with relevant regulations.
7. Adaptability to New Technologies: The platform continuously integrates the latest OSINT and AI technologies, keeping pace with evolving digital landscapes and information sources. By leveraging these capabilities, KIS helps intelligence agencies effectively harness the power of OSINT while addressing its inherent challenges.
Scenarios for Intelligence Agencies Using OSINT

Counterterrorism
Intelligence agencies use OSINT to monitor online radicalization, track
the dissemination of extremist content, and identify potential threats before
they materialize. This involves scanning forums, social media platforms, and
even encrypted messaging apps for signs of terrorist activities.
Cybersecurity
OSINT is crucial in identifying cybersecurity threats. Agencies can
monitor hacker forums, track the sale of stolen data on the dark web, and
analyze malware strains to predict and prevent cyberattacks.
Election Monitoring
OSINT is used to ensure the integrity of elections by monitoring social
media for signs of disinformation, tracking the influence of foreign actors, and
analyzing voting patterns to detect irregularities.
Humanitarian Aid
In disaster-stricken areas, OSINT helps in assessing the situation on
the ground, identifying the most affected areas, and coordinating the delivery
of aid. Satellite imagery, social media posts, and news reports provide
real-time updates that are critical for effective response.
OSINT Methodology and Process
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) is a structured and systematic approach to gathering and utilising publicly available information from various online sources. The OSINT methodology follows a well-defined lifecycle that encompasses planning, data collection, processing, analysis, reporting, and action.
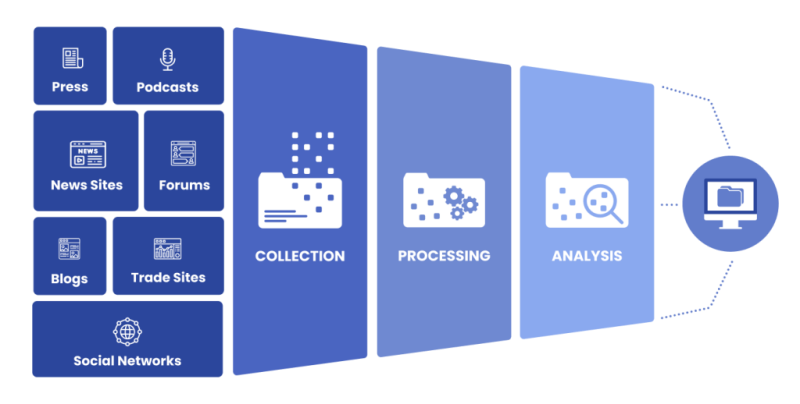
The OSINT Lifecycle
The OSINT process is often represented as a cyclical lifecycle, reflecting the
iterative nature of information gathering and analysis. This lifecycle consists
of the following stages:
· Planning and Objective Setting: Define the purpose of
your OSINT activity, whether it’s threat detection, competitive analysis, or
investigative research. Set clear objectives, outline the scope of your
investigation, and identify the types of information you need to gather.
· Data Collection: Gather data from various publicly
available sources, such as websites, social media platforms, online databases,
and public records. Cast a wide net to ensure comprehensive coverage of your
subject matter.
· Data Processing and Analysis: Organise and process
the collected data to extract relevant information. Analyse the data for
patterns, connections, and insights. This stage involves filtering out noise and
identifying key data points that align with your objectives.
· Reporting and Action: Compile your findings into a
structured report that communicates the insights derived from your analysis. The
report should provide clear and actionable recommendations based on the OSINT
data. The information can inform decision-making, threat mitigation, or
strategic planning.
The OSINT lifecycle is iterative, meaning that the insights gained from
one cycle can inform and refine subsequent cycles. As the digital landscape
evolves and new data becomes available, OSINT practitioners continuously iterate
through this process to stay current and adapt to emerging trends.
1. Planning and Objective Setting
Effective OSINT activities begin with careful planning and objective
setting. This stage involves:
· Identifying the purpose of your OSINT effort, whether it’s related to
cybersecurity, business intelligence, or investigative research.
· Defining clear and measurable objectives that guide your data
collection and analysis efforts.
· Outlining the scope of your investigation, including the specific
topics, entities, or events you intend to study.
· Identifying potential data sources and techniques that align with your
objectives.
Proper planning ensures that your OSINT efforts are focused, efficient,
and aligned with your goals. It helps prevent data overload and ensures that the
collected information is relevant and valuable.
2. Data Collection
Data collection involves gathering information from a diverse range of
sources. These sources may include:
· Publicly accessible websites and web pages.
· Social media platforms, including posts, profiles, and discussions.
· Online forums, blogs, and discussion boards.
· News articles and press releases.
· Public records, government databases, and court documents.
· Geolocation and mapping data.
· Specialised search engines and data repositories.
Effective data collection requires employing a combination of search
techniques, tools, and resources to ensure comprehensive coverage. It’s
essential to validate the credibility and authenticity of the sources to ensure
the accuracy of the collected data.
3. Data Processing and Analysis
Once the data is collected, it needs to be processed and analysed to
extract meaningful insights. This stage involves:
· Cleaning and organising the data to remove duplicates, irrelevant
information, and noise.
· Applying filters and sorting mechanisms to focus on relevant data
points.
· Identifying patterns, connections, and trends within the data.
· Cross-referencing information from multiple sources to verify
accuracy.
· Extracting actionable intelligence that aligns with your objectives.
Data processing and analysis require critical thinking, attention to
detail, and the ability to draw meaningful conclusions from the collected
information. Various analytical tools and techniques can aid in this process,
such as data visualisation, link analysis, and sentiment analysis.
4. Reporting and Action
The final stage of the OSINT process involves creating a comprehensive
report that communicates your findings and recommendations. A well-structured
report should include:
· Executive summary: A concise overview of the key findings and
recommendations.
· Methodology: Explanation of the data collection and analysis methods
employed.
· Insights: Presentation of the discovered patterns, trends, and
connections.
· Visualisations: Graphs, charts, and diagrams that enhance
understanding.
· Recommendations: Actionable steps based on the insights derived from
the OSINT analysis.
Social Media Resources of OSINT for Intelligence Agencies
TweetDeck
TweetDeck is a social media dashboard application for managing multiple
Twitter accounts. It is an essential OSINT tool for intelligence agencies to
monitor real-time conversations, track hashtags, and analyze trends related to
specific geopolitical events or security threats.
Social Searcher
Social Searcher enables real-time social media search, helping
intelligence agencies detect trends, identify key influencers, and monitor brand
reputation or online movements, which are crucial in counter-terrorism and
crisis management.
Twint
Twint is an advanced Twitter scraping tool that gathers data without
using Twitter's API. It's particularly useful for intelligence agencies tracking
accounts, tweets, and public sentiment without login limitations or API
restrictions.
Websites of OSINT for Intelligence Agencies
IntelTechniques
A comprehensive platform offering OSINT tools, techniques, and a
specialized search engine. This site provides valuable resources for
investigating various open-source data such as social media profiles, email
addresses, and phone numbers.
Pipl
Pipl is a people search engine that helps find personal, professional,
and social media profiles. It is used by intelligence agencies to verify
identities, track individuals, and gather intelligence on targets.
Have I Been
Pwned
This site alerts users to data breaches. Intelligence agencies use it to
track compromised accounts and identify personal information that has been
exposed in cyber attacks.
ODNI and CIA Release the Intelligence Community OSINT Strategy for 2024-2026

On March 8, 2024, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) and
the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) today released the Intelligence Community
(IC) Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) Strategy for 2024-2026.
OSINT, or intelligence derived exclusively from publicly or commercially
available information that addresses specific intelligence priorities,
requirements, or gaps, is vital to the IC’s mission, providing unique
intelligence value and enabling all other intelligence collection disciplines.
Given the expansive and evolving open source environment, the IC has been
working to modernize its approach to collecting, creating, and delivering OSINT,
and the IC OSINT Strategy outlines the way forward.
“The IC OSINT Strategy represents the beginning of a long-term process
that will professionalize the OSINT discipline, transform intelligence analysis
and production, and create new avenues for partnering with brilliant American
innovators and like-minded foreign partners,” said Director of National
Intelligence Avril Haines.
“As the IC’s Functional Manager for OSINT, I know the critical role that
OSINT plays in defending our country and values,” said CIA Director William J.
Burns. “In this pivotal moment, when OSINT is increasingly important and growing
in demand, an IC-wide OSINT strategy is key to helping the IC move forward in a
coordinated and determined way.”
Conclusion
OSINT has become an integral part of intelligence operations, offering a cost-effective, accessible, and efficient means of gathering and analyzing information. By leveraging the power of publicly available data, intelligence agencies can enhance their situational awareness, respond to emerging threats, and make informed decisions. As technology continues to evolve, the role of OSINT in intelligence will only grow, making it a critical component of modern intelligence strategies.