10 Popular Free Open Source Intelligence Platforms
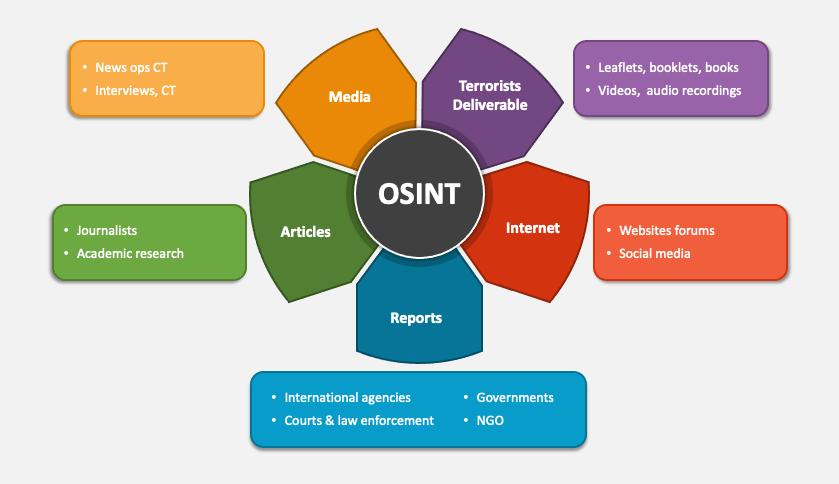
OSINT Definition
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) refers to the practice of gathering information from publicly accessible sources. Whether utilized by IT security professionals, malicious hackers, or government intelligence operatives, OSINT involves sophisticated techniques to sift through vast amounts of visible data to uncover specific, valuable information.
OSINT is often considered the counterpart to operational security (OPSEC). OPSEC is the process by which organizations safeguard public data that, if analyzed correctly, could expose sensitive information. Internal security teams conduct OSINT operations on their organizations to enhance operational security. They identify sensitive information that might be inadvertently public, allowing them to secure exposed data and predict what an attacker might know. This information is crucial for risk assessment, resource prioritization, and improving security practices and policies.
In this context, "open source" refers to the public availability of the data being analyzed, not to the open-source software movement, although many OSINT platforms are indeed open source.
OSINT History: From Spycraft to IT
During the 1980s, military and intelligence agencies began shifting some of their information-gathering efforts from covert activities, such as reading adversaries' mail or phone tapping, to seeking intelligence that was publicly available or officially published. This change was partly due to the evolving global landscape, where even without social media, numerous sources like newspapers and public databases contained valuable information for those adept at connecting the dots. The term OSINT was coined to describe this type of intelligence gathering.
These techniques are now applicable to cybersecurity. Modern organizations often have extensive public-facing infrastructures spread across various networks, technologies, hosting services, and namespaces. Information can be found on employee desktops, legacy on-prem servers, employee-owned devices, cloud storage, embedded devices like webcams, or even within the source code of active applications. Security and IT staff at large companies frequently lack comprehensive knowledge of all assets within their enterprise, public or otherwise. Many organizations also control additional assets indirectly, such as social media accounts, leading to significant information exposure that could be exploited if it falls into the wrong hands.
Why is OSINT Important?
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) is vital for managing the vast amount of publicly available information. IT departments need to fulfill three key tasks within OSINT, and a variety of platforms have been developed to support these needs. While many platforms cover all three functions, some excel in specific areas.
Discovering Public-Facing Assets
One of the primary roles of OSINT is to help IT teams identify public-facing assets and map out the information these assets reveal, which could be exploited in a potential attack. The main focus here is on documenting what can be publicly discovered about company assets without engaging in hacking activities. This does not include identifying program vulnerabilities or conducting penetration tests but rather understanding the publicly accessible information about the organization.
Finding Relevant External Information
Another critical function of some OSINT platforms is to search for pertinent information outside the organization. This includes monitoring social media posts and examining domains and locations that may fall outside a narrowly defined network. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that have undergone mergers or acquisitions and need to integrate the IT assets of the acquired companies. Given the widespread use and influence of social media, monitoring external information is advantageous for nearly every organization.
Aggregating Discovered Information into Actionable Intelligence
Lastly, certain OSINT platforms are designed to aggregate and organize all the discovered information into actionable intelligence. Conducting an OSINT scan for a large enterprise can produce vast amounts of data, especially when both internal and external assets are considered. These platforms help prioritize and address the most critical issues first, making it easier for organizations to manage and respond to potential threats effectively.
Evolution of OSINT Platforms
The evolution of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) platforms has been remarkable. Initially, these platforms focused on traditional media analysis, including newspapers and radio broadcasts. Over time, OSINT platforms have adapted to leverage the immense data available on the internet, spanning both private and public sectors.
Modern OSINT platforms have progressed beyond simple search engines. They now include sophisticated analytical and visualization capabilities. By integrating cutting-edge technologies like web scraping, social media analytics, and geospatial intelligence, these platforms have transformed the methods of extracting and assessing information.
The future of OSINT platforms is poised to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, which will enhance the precision and speed of data processing and analysis.
Top OSINT platforms come with advanced features that significantly improve the intelligence gathering process. One such feature is built-in data transformations, which convert retrieved information into more usable or readable formats. Additionally, many OSINT platforms offer custom transformation capabilities, allowing users to tailor data collection and analysis to their specific needs.
10 Popular Free OSINT Platforms
There are numerous free OSINT platforms available for individuals and organizations to start using today. These platforms cover a wide range of capabilities and can be used for various intelligence-gathering purposes.
Google Dorks
Google Dorks, in use since 2002, offer specialized queries that harness Google's vast indexing to aid in security investigations. These queries can locate specific file types, extensions, text within pages, titles, and URLs — tools invaluable for exploring details about individuals and companies. Despite search engines typically not indexing sensitive data like log files, Google Dorks can still unearth such information, providing a critical resource for IT security.
theHarvester
Included in the Kali Linux distribution, theHarvester is a comprehensive platform used to gather information about subdomains, virtual hosts, open ports, and email addresses related to any company or website. It utilizes sources such as PGP key servers, search engines like Google and Bing, and social networks like LinkedIn to collect data, supporting both passive reconnaissance and active penetration tests. This platform is particularly useful for the initial stages of penetration testing on both local and third-party authorized networks.
SecurityTrails
The SecurityTrails API allows instant access to current DNS server records and historical records (known as DNS history), domain details, associated domains, IP information, as well as WHOIS data. This data can be integrated within your own applications for asset discovery, threat intelligence, risk scoring, and more. The best part is that you only need an HTTP request to retrieve the data.
BGPView
Effortlessly track BGP routing information and IP address data with BGPView, simplifying network monitoring tasks. Analyze network configurations, identify security threats, and monitor routing changes seamlessly. This intuitive network platform offers comprehensive insights accessible directly from your browser, enabling informed decisions to optimize network performance, identify threat actor origin, and much more.
Recorded Future
Access detailed vulnerability information from this free CVE database. This platform provides invaluable insights for security teams to stay ahead of emerging CVEs. It includes useful information such as CVSS score, Attack Complexity level, Availability, a summary of each CVE, along with affected products and mitigation resources.

Triage
Explore malware samples for free with one of the most advanced and popular malware analysis sandboxes. This platform offers a customizable environment where you can submit high volumes of malware samples, enabling detection and extraction of configurations for a wide range of malware families.
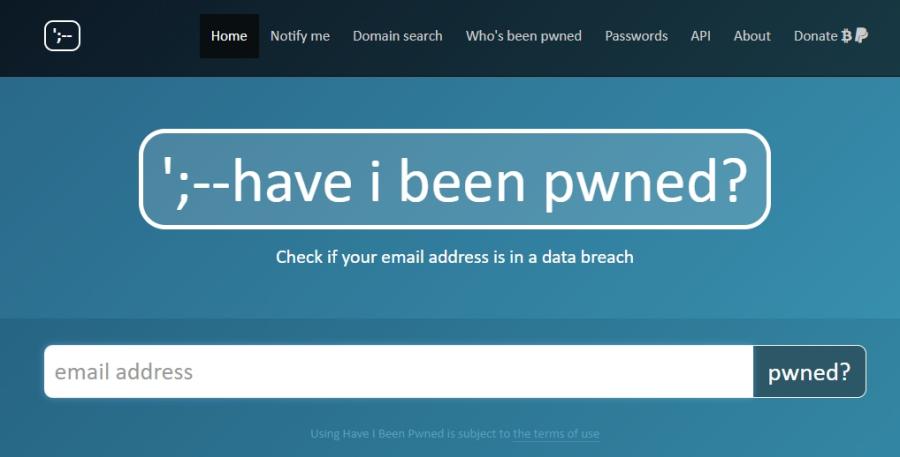
Have I Been Pwned?
HaveIbeenPwned can help you to check if your account has been compromised in the past. This site, developed by Troy Hunt, one of the most respected IT security professionals, has been serving accurate reports for years. If you suspect your account has been compromised, or want to verify for 3rd party compromises on external accounts, this is the perfect platform. It can track down web compromises from many sources like Gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo accounts, as well as LastFM, Kickstarter, Wordpress.com, Linkedin and many other popular websites.
Shodan
Conceived by John Matherly in 2009, Shodan serves as a network security monitor and specialized search engine for the deep web and IoT. It enables users to explore a plethora of network-connected devices, organizing results by country, operating system, and network type, providing invaluable insights for IT security researchers.
SpiderFoot
Developed by Steve Micallef, SpiderFoot stands out as a top reconnaissance platform for automating OSINT with swift results in reconnaissance, threat intelligence, and perimeter monitoring. It harnesses over 100 public data sources to gather intelligence on various targets, including generic names, domain names, email addresses, and IP addresses, simplifying the process through easy-to-use module selection and target specification.
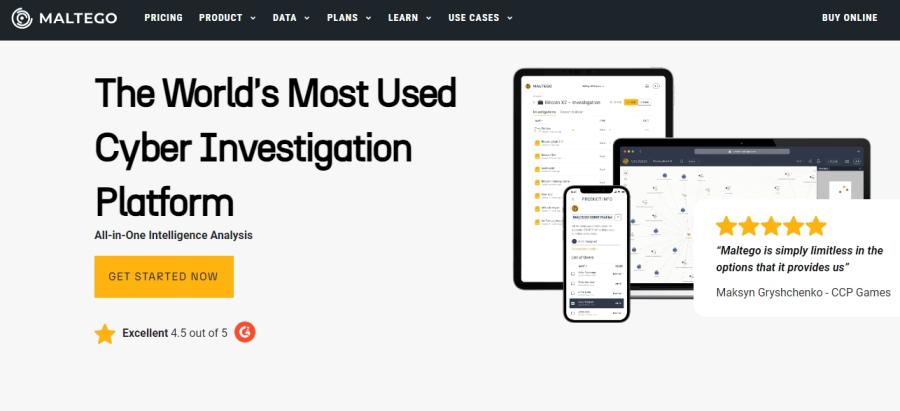
Maltego
Developed by Paterva and featured in the Kali Linux distribution, Maltego is a robust platform designed for detailed digital reconnaissance of targets. It utilizes "transforms" to integrate and analyze data from external applications, available in both free and commercial versions. Users can launch investigations to obtain comprehensive results, such as IPs, domains, and AS numbers, through Maltego's platform.
Is OSINT Illegal?
While OSINT techniques can be utilized by malicious hackers for reconnaissance prior to launching illegal attacks, the platforms and techniques themselves are generally legal. These methods are designed to help users locate publicly accessible data. Government agencies also use OSINT techniques to identify vulnerabilities in their cybersecurity defenses.
However, following the trails revealed by OSINT queries can sometimes lead to legal grey areas. For example, it is legal to access public areas of the dark web to check if your organization's data has been breached. Yet, buying stolen data or impersonating law enforcement to extract information from shady characters is illegal.
To avoid legal pitfalls, it's essential to develop a code of conduct that guides employees' behavior during OSINT activities and document all actions taken. This documentation helps ensure adherence to legal guidelines and demonstrates compliance with established protocols.