Steps to perform Twitter sentiment analysis
1. Collect Twitter data
Collecting information from Twitter
must take into account both current tweets and historical tweets.
Data from
current tweets can be used to track keywords or subject tags in real time, and data
from historical tweets is valuable for comparing sentiment across time.
2. Prepare the data
After selecting relevant tweets
for sentiment analysis, it's time to prepare the data. It is important to manage the
data when selecting it to perform a study or sentiment analysis. The better the
quality of the selected content, the better the results will be.
Irrelevant
information or content needs to be removed, such as emojis, extra spaces, irrelevant
quotes, etc. For example, as part of the preparation, an in-depth investigation
should be conducted to exclude duplicate or bot-generated tweets.
3.
Sentiment analysis of data
Tweets that qualify for quality
research can now be submitted to sentiment analysis tools for investigation.
Visualization of results
Sentiment analysis exposes
the data obtained by generating KPI results through graphs. There are two distinct
approaches to visualizing real-time analytics - basic text analytics or geospatial
real-time analytics.
Real-time Basic Text Analysis
Analyzing
text and sentiment ratings in tweets in real time is a challenge because you have to
process and rate the data in a streaming fashion. Generating influencer dashboards
in this use case is also basic, as other data points such as "location" and
influencer ranking are not considered here.

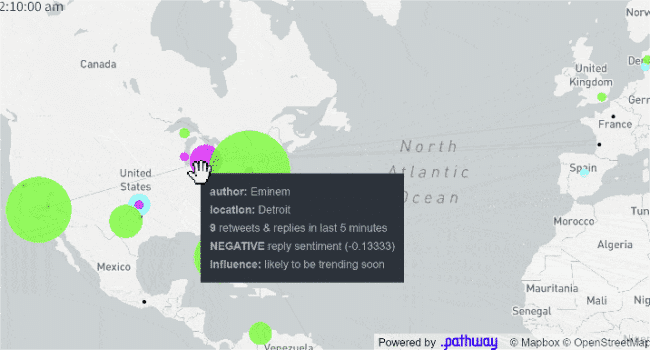
Real-time Geospatial Analytics
For global brands, it's
important to know what's happening globally. Brand reputation can be managed through
regional representation and communication protocols, with a focus on customer
expectations. Understanding "outbreaks" and trends in a Google-like mapping
interface makes it easy to understand how different customers in different regions
and cultures are interpreting events. This can quickly become very complex as you
deal with streaming data (text and geospatial data), machine learning and reactive
dashboards.