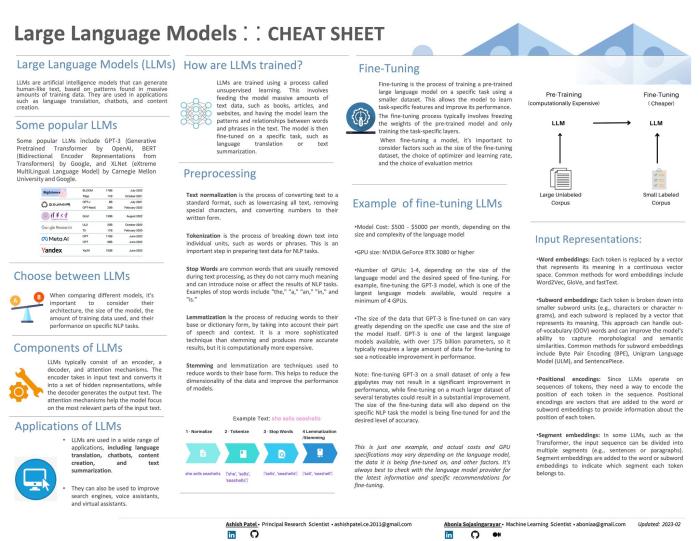
What is a Large Language Model?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an artificial intelligence model trained by deep
learning algorithms to recognize, generate, translate, and/or summarize large
amounts of written human language and text data. Large Language Models are one of
the most advanced and easy-to-use natural language processing (NLP) solutions
available today.
Large Language Models have a wide range of applications,
including language translation, chatbot and content creation, text summarization,
and can also be used to improve search engines, voice assistants, and virtual
assistants.
How do large language models work?
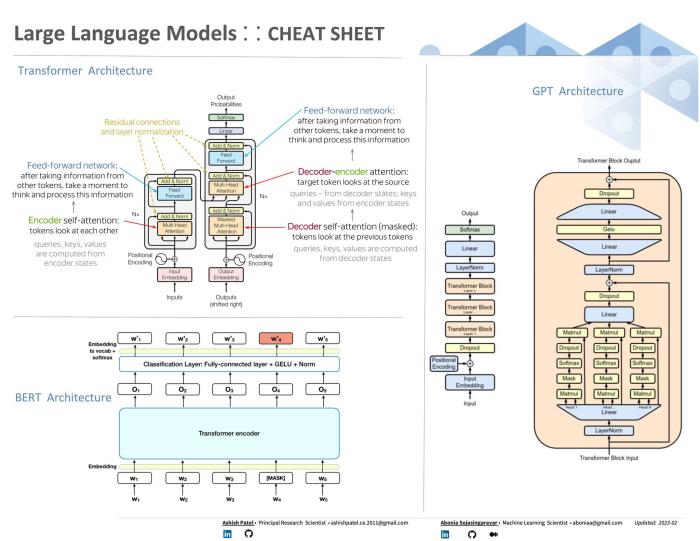
Large
language models work primarily through their specialized converter architecture and
large training data sets.
For a large language model to work, it must first
be trained on a large amount of textual data to make context, relationships, and
text patterns clear. This data can come from many sources, such as websites, books,
and historical records. wikipedia and GitHub are two of the larger web-based samples
used for LLM training. Regardless of the source, the training data must be cleaned
and quality-checked before it can be used to train the LLM.
Once the data is
cleaned and ready for training, it can be tokenized, or broken down into smaller
parts for easier understanding. Tokens can be words, special characters, prefixes,
suffixes, and other linguistic components that make contextual meaning clearer.
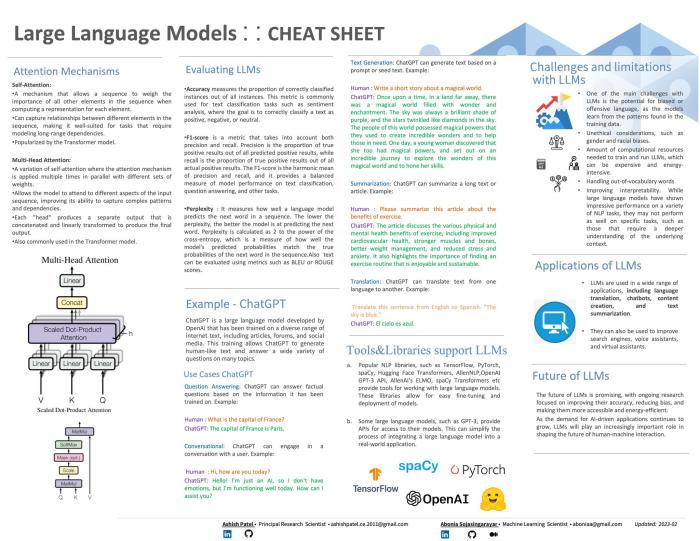
Tokens also inform the attention mechanism of the large language model, or its
ability to quickly and intelligently focus on the most relevant parts of the input
text so that it can predict and/or generate appropriate output.
Once a large
language model has received initial training, it can be deployed to users through
various forms, including chatbots. However, enterprise users access large language
models primarily through APIs that allow developers to integrate LLM functionality
into existing applications.
Large Language Models are trained primarily
through unsupervised, semi-supervised, or self-supervised learning, and LLMs can
adjust their internal parameters and effectively "learn" from new user input over
time.