The 12 Most Frequently Exploited Vulnerabilities in 2022 (2)
Related:
The 12 Most
Frequently Exploited Vulnerabilities in 2022 (1)
5.
Microsoft Various Products (CVE-2022-30190)
CVE-2022-30190, known
as "Follina", is a critical RCE vulnerability that affects multiple Microsoft Office
products. Follina allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code after convincing a
user to open a malicious Word document or any other vector that handles URLs. Due to
the large number of unpatched Microsoft Office products available, Follina continues
to appear in various cyberattacks.
Known threat actors exploit the Follina
vulnerability through phishing scams that use social engineering techniques to trick
users into opening malicious Office documents. When a user encounters embedded links
within Office applications, these links are automatically fetched, triggering the
execution of the Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) protocol, a Microsoft
service that is primarily used to collect system crash information for reporting to
Microsoft Support. However, threat actors can exploit this protocol by crafting
links to enforce the execution of malicious PowerShell commands without any further
user interaction. This poses a serious security risk as it allows attackers to
remotely execute unauthorized commands on the target system via seemingly innocuous
links.
Recently, the Follina vulnerability has been used as a zero-day
exploit to support threat campaigns against key industry organizations. From March
through May 2022, an active cluster tracked as UNC3658 used Follina to attack the
Philippine government. In April of the same year, more Follina samples appeared in
the UNC3347 campaign targeting telecom entities and business services in South Asia.
A third cluster named UNC3819 also used CVE-2022-30190 to attack organizations in
Russia and Belarus.
6. Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus
(CVE-2021-40539)
A patched critical vulnerability in the Zoho
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus software in late 2021 led to attacks on at least
nine entities in the defense, healthcare, energy, technology and education sectors.
The product is said to provide a comprehensive self-service password management and
single sign-on (SSO) solution for Active Directory and cloud applications, designed
to allow administrators to enforce two-factor authentication (2FA) for secure
application logins while granting users the ability to reset their passwords on
their own.
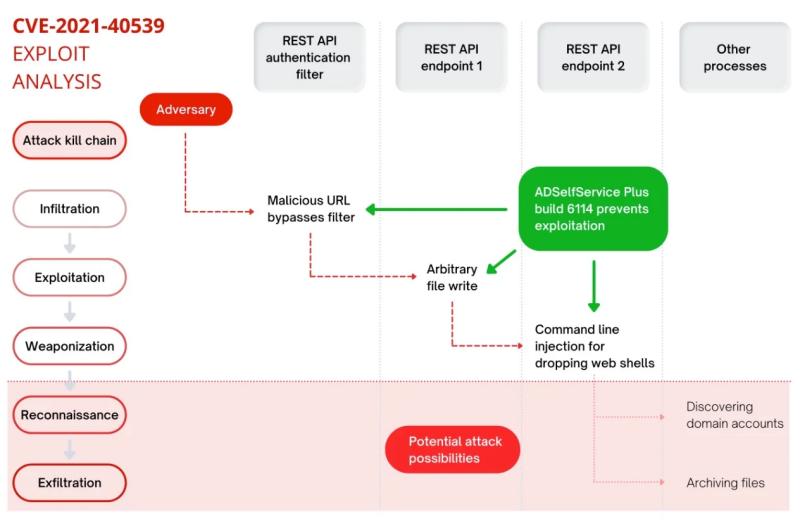
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2021-40539, allows threat
actors to gain initial access to a victim organization's system.CVE-2021-40539 (CVSS
score 9.8) is an authentication bypass vulnerability that affects REST API URLs that
can be used for RCE.
In response, CISA issued an alert about the zero-day
vulnerability, informing users how attackers could exploit the vulnerability to
deploy web shells for post-exploitation activities such as stealing administrator
credentials, performing lateral moves, and leaking registry and Active Directory
(AD) files. The vulnerabilities are particularly acute in SSO solutions for AD and
cloud applications. If these vulnerabilities are successfully exploited, attackers
can essentially access critical applications, sensitive data, and other areas deep
within the corporate network via AD.
Vulnerabilities exploiting CVE-2021-40539 were also recently discovered in an attack against the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC). In a statement, the ICRC acknowledged that they missed critical patches that could have protected them from the attack, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a robust patch management process. As a result of the attack, the names, locations and contact information of more than 515,000 people involved in the ICRC's Restoring Family Links program were compromised.